How Does E-Coating Work?
Electrocoating, or commonly referred to as E-coating is the method of applying paint to a substrate in a paint bath. To find out more about what electrocoating is click here.
The e-coating process can best be described as a cross between plating and painting. Read on to find out how e-coating works and how water is part of the electrocoating process.
How Does E-Coating Work?
The coating materials such as resins, pigments, additives are dispersed in water and circulated in a bath. The parts to be coated are immersed in the solution and electrical current (from anodes) is passed through the bath using the parts as an electrode. That’s how e-coating works.
Electrical activity around the surface of the parts makes the resin directly in contact become insoluble in water.
This then causes a layer of resin – including any pigments and additives present – to adhere to the surface of the parts.
The coated parts can then be removed from the bath. The next step is to remove any excess paint known as cream-coat. This is carried out in the flowing post rinses of ultrafiltration.
Ultrafiltrate is a by product of the paint going through a membrane, filtering the paint creating permeate. This is part of a closed loop system to keep tank levels at their optimal.
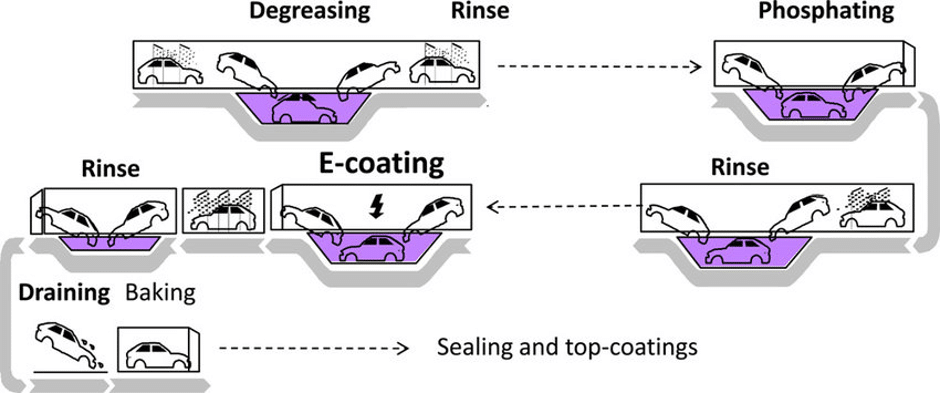
The Ecoat process typically involves a number of stages including a cleaning stage followed by a phosphate conversion coating. This enhances the corrosion resistance of the metal, it also provides an improved base for the subsequent coating.
Only after the metal is properly prepared can the electropainting process take place. This is then followed by the post rinse ultrafiltrate and then oven curing stage.
How Is Water A Part Of The Electrocoating Process?
E-coating can be seen as a simple 4 step process; pre-treatment, coating, post-rinse and curing, however realistically there are many other steps. The pre-treatment alone can consist of 8 or 9 steps; repeating chemical treatment, also known as phosphating, and rinses. Within each rinse, high quality water is required, from a water filtration system such as Reverse Osmosis.
When a metal part is first formed it will have impurities such as grease, oil and grime on it. This needs to be washed off before any paint can be applied or it may affect the finish.
This is why the pre-treatment process is so complex, the substrate is not rinsed with just water but instead chemicals and acid are also added to the solution to clean the product.
Pure water is then used between each chemical rinse to remove any residue or excess sealant, preparing the part for the next chemical treatment.
Once the part has been rinsed and correctly treated it’s time for the car frame to be submerged into the ecoat tank. The e-coat paint bath is made up of around 80% pure water and 20% paint.
Tubular Anodes ensure the electric current remain the same throughout the coating process – this ensures the paint is stuck onto the part equally.
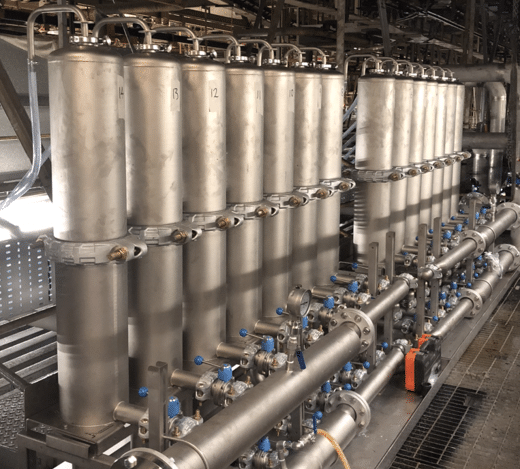
Exclusive to Membracon is an Ultrafiltration Flexoperm System making membrane replacement much more efficient.
Anolyte systems flush the anode tubes within the paint bath, this is to get rid of high acidic solution and keep the anodes at their optimal performance.
Within this system Reverse Osmosis can provide the pure, high quality water that can be used throughout the process, providing a base for the chemical and paint tanks and also for the rinse tanks.
Conclusion
To conclude, e-coating is an immersion wet paint finishing process. It uses an electrical current to attract the paint product to the metal part. The process includes many steps with rinses and coatings repeated.
The reason the parts need to be rinsed between coats is to ensure no excess residue, bits of metal, grease or oil is left on the part. E-coating is commonly used in the automotive sector, making a mistake with a car body could be detrimental to finished product.
That’s why it’s so important to have the correct water production and water filtration systems in place at different stages of the production line.
To find out more about the equipment and membranes available for e-coating or to request a quote, get in touch today. Membracon’s water experts treat each individual project separately- only recommending the appropriate equipment that will work for your unique process.